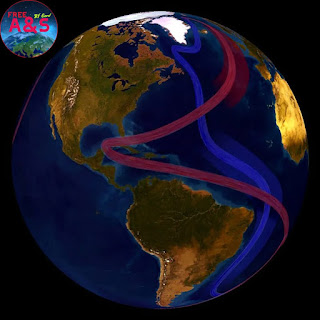
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation is part of this complex system of global ocean currents that circulates cool subsurface water and warm surface water throughout the world. Image credit: NOAA
Understanding the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)
The AMOC is an integral part of the world's ocean conveyor belt, a complex global system of ocean currents that circulate cool subsurface water and warm surface water throughout the planet.
The AMOC plays a pivotal role in the distribution of heat and freshwater across the Atlantic through an intricate network of deep and shallow ocean currents. This system transports warm and salty surface water from the tropics to the North Atlantic.
As this water approaches the North Pole, it cools down and forms sea ice. The remaining water then sinks and travels southwards in the deeper ocean layers, thus completing the cycle. This circulation is vital for regulating the Earth's climate, and any significant changes could have profound implications.
The Role of AMOC in Regulating Climate
By carrying warmer waters towards the North Pole, the AMOC fosters warmer weather conditions in Northwest Europe and the North Atlantic. In the absence of the AMOC, these regions would be considerably colder.
The AMOC's influence isn't limited to temperature regulation. It also affects rainfall patterns, sea-level changes, and even the health of marine ecosystems. Therefore, understanding the stability of the AMOC is vital for predicting future climate scenarios.
The Threat of Climate Change
There's a growing concern that climate change could irreversibly disrupt the AMOC. Numerous studies have suggested that the AMOC's flow is slowing down, operating at its weakest rate in centuries.
Most climate models predict that the AMOC will continue to weaken as the climate crisis intensifies. However, the extent and speed of this decline are subjects of ongoing debate. Some research suggests that the AMOC could collapse within decades, or even years, a claim that has ignited controversy within the scientific community.
Predicting the Tipping Point
Researchers at Utrecht University in the Netherlands have recently developed a new method to detect early warning signals that the AMOC is nearing its tipping point.
By running a comprehensive computational model that simulates the flow of surface freshwater around the North Atlantic over 2,200 years, they discovered a vital indicator. They found that the movement of freshwater in the Atlantic around the 34th parallel south could help predict an imminent collapse in the AMOC.
The researchers used the minimum volume of freshwater being shifted northward from this southern part of the Atlantic to determine if the AMOC would collapse in the next 20 years.
The Verdict
When the model's findings were compared with real-world data, it confirmed what most other models have been indicating: the AMOC is on the brink of a tipping point.
The researchers wisely refrained from providing a precise timeline for the potential tipping point. Still, they noted that the collapse of the AMOC would dramatically alter the distribution of heat across the world's oceans and beyond.
Implications of the AMOC Collapse
The collapse of the AMOC would have far-reaching implications for our planet's climate. It could lead to a significant decrease in temperatures in the North Atlantic region, potentially triggering severe weather events and affecting marine biodiversity.
Moreover, the disruption of heat distribution could influence global rainfall patterns, potentially leading to extreme weather events such as droughts and floods. Such drastic changes would not only affect ecosystems but also impact agriculture, water resources, and ultimately, human livelihoods.
Looking Ahead
Although the potential collapse of the AMOC paints a grim picture, it is important to remember that this is not yet a certainty. Scientists continue to monitor and research this critical climate factor, aiming to refine their predictions and enhance our understanding of the potential impacts.
Climate change is undeniably a global challenge requiring urgent collective action. The potential collapse of the AMOC serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet's systems and the profound impact that human activity can have on these delicate balances.
Conclusion
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation is an essential component of our planet's climate system. The potential collapse of this 'ocean conveyor belt' due to climate change could have dramatic implications, from altering global temperatures to disrupting rainfall patterns.
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of our planet and the impacts of climate change, one thing becomes increasingly clear: our actions today will shape the world of tomorrow. It's up to us to decide what kind of future we want to create.
Remember, the journey of scientific discovery is a shared one, and everyone is invited. Stay curious, keep learning, and together, let's explore the wonders of the universe.
Stay tuned for more fascinating insights from the world of science!
The new study is published in the journal Science Advances.

Post a Comment